Page 11 - Reflections_dyslipidaemia_newsletter4_2023
P. 11
REFLECTIONS
Dyslipidaemia
Dyslipidaemia Global Newsletter #4 2023
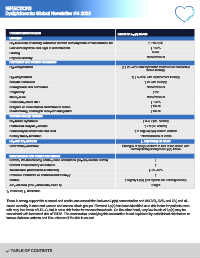
Condition/intervention Effect on Lp(a) levels Dyslipidaemia
Lifestyle
Replacement of dietary saturated fat with carbohydrate or unsaturated fat ↑ ~10–15%
Low carbohydrate diet high in saturated fat ↓ ~15%
Fasting None
Physical activity None/minimal
Hormones and related conditions
Hyperthyroidism ↓; ↑ 20–25% with thyrostatic treatment or radioactive
iodine therapy
Hypothyroidism ↑; ↓ 5–20% with replacement therapy
Growth hormones ↑ 2x with therapy
Endogenous sex hormones None/minimal
Pregnancy ↑ 2x
Menopause None/minimal
Postmenopausal HRT ↓ ~25%
Surgical or biochemical castration in males ↑ Small
Ovariectomy, oestrogen receptor antagonist ↑ Small
Chronic kidney disease
Nephrotic syndrome ↑ 3–5 x (vs. control)
Peritoneal dialysis patients ↑ 2 x (vs. control)
Hemodialysis treatment and CKD ↑ in large apo(a) isoform carriers
Kidney transplantation ~Normalization of levels
Hepatic impairment ↓, depending on cause
Liver transplantation Changes of apo(a) isoform to that of the donor, with
corresponding changes in Lp(a) levels
Inflammation and related conditions
Severe, life-threatening acute-phase conditions (sepsis, severe burns) ↓
Several inflammatory conditions ↑
Tocilizumab (interleukin-6 inhibitor) ↓~30–40%
Protease inhibitors or antiretroviral therapy ↑
Statins ↑ slightly Lp(a) (but reports are heterogeneous)
Air pollution (fine particulate, PM 2.5) ↑Slight
↑, increase; ↓, decrease.
There is strong support for a causal and continuous association between Lp(a) concentration and ASCVD, AVS, and CV, and all-
cause mortality in men and women and across ethnic groups. Elevated Lp(a) has been identified as a risk factor for patients even
with very low levels of LDL-C, but is not a risk factor for venous thrombosis. On the other hand, very low levels of Lp(a) may be
associated with increased risk of T2DM. The mechanism underlying this association is not explained by established risk factors or
known diabetes variants and it is unknown if the risk is causal.
TABLE OF CONTENTS